Current Research Projects
Our studies deal with a variety of matrices - surface water, wastewater, seawater, biological, bacteria, sludge and soil in order to explore and understand the pollutants effects and the potential for treatment.
For more details on each research project, visit the Water Research Center active research lobby.

Coral reef structure is strongly influenced by illumination. Corals are highly photosensitive and many species synchronize their spawning through detection of low light intensity from moonlight. Therefore, light pollution is likely altering the structure and functioning of marine ecosystems in many other ways that have yet to be explored. This research is focus on how the artificial light pollution in Eilat is affecting coral reproduction, hormonal secretion, recruitment phylogeny and gene connectivity along the shoreline of the Golf Of Eilat/Aqaba from north to south.

Natural atmospheric precipitation might consider as a possible alternative for reducible traditional water sources. The use of atmospheric precipitation as alternative water resource raised the significant issue of public health risks associated with air pollution and microbiological pollutants, and determine the need of analysing their quality. In this research, we are studying the circumstantial relation between air pollution and atmospheric water contamination through various issues.

Plastic fragments and drugs residues polluting the ocean are increasing significantly each year, having a devastating effect on the marine environment. Ascidians are marine sessile filter-feeding invertebrates which are very common around the world. filtering high volumes of water, ascidians have a unique potential to act as a natural biological filter for contaminants like micro-plastic, phthalates and drugs residues. An innovative analyitical methods are developed to extract and detect drugs and phthalates from the organism's body.

Chemotherapic drugs flush into the municipal wastewater because hospitals are not required to pre-treat their sewage before it enters the municipal WWTP. Advanced oxidation process (AOP) have the potential to degrade those compounds. Their identification in wastewater is possible using a HPLC-MS methods. The research objective is to develope analytical method to identify, concentrate and quantitate selected chmotherapic drugs, focusing on effluent matrix.
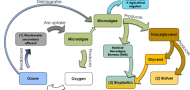
The goal of this project is to demonstrate a circular economy model, based on the biorefinery concept, enabling an ecofriendly alternative by producing biofuels, separating the lipids and the residual microalgae biomass processed into bioplastics and uptake of plasticizers and from wastewater. This concept will be used by implementing green technologies and green concepts that allow improving the utilization of microalgae products.
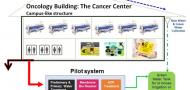
The objective of this study is to promote local and efficient treatment of hospitals wastewater in Israel and abroad before discharging them into the municipal WWTP. The suggested treatment includes combination of biological, physical and chemical processes. This will improve the quality of Israel's water sector, which is based in part on reclaimed water for irrigation purposes and will prevent an environmental pollution of the water sources.

Membrane technologies of effluent reverse osmosis as the main reclamation process, seems to enlarge due to growing wastewater quantities, water shortage and land area limitation. Wastewater RO concentrate is the harmful byproduct and the bottleneck for wide reverse osmosis implementation, as it requires a special treatment before being discharged to the environment. This research focuses on the most effective technology for micro-pollutant removal - advanced oxidation processes (AOP).
Studies show that up to 80% of the drugs we take, leave our bodies and reaching to municipal wastewater. Many of those pharmaceuticals residues, affecting plant, animal and human health when they re-enter the water cycle. This is the reason it needs to be taken care before it drains to the municipal plants. It is likely that during the treatment process, we can recapture and re-use these pharmaceuticals. By recover a useful pharmaceuticals from hospitals’ wastewater, we will turn the wastewater treatment, a cost-efficient procedure of a clean technology.

