Identification and Examination of removal efficiency of six therapeutic drugs and anti-inflammatory medication derived from the Oncology Building at ‘Tel Ha'Shomer' Hospital
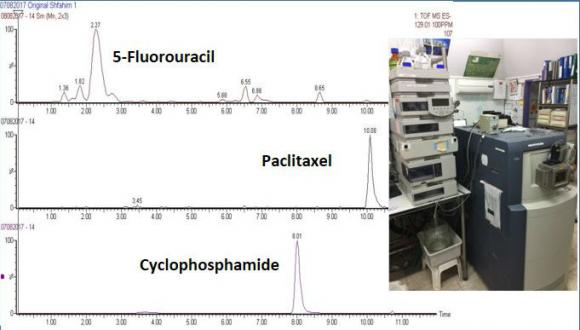
Analytical method development to identify and quantify six chemotherapy drugs in the wastewater
Analytical method development to identify and quantify six chemotherapy drugs in the wastewater
The Problem:
Therapeutic drugs’ mechanisms of action are based on interactions with the cell or it’s DNA.
Most of them remain unchanged after being administrated to the body, meaning they remain toxic as they exit the human body (via excretion).
Therapeutic drugs enter the WWTP (Waste Water Treatment Plant) because Hospitals are not required to pre-treat their sewage before it enters the municipal waste water systems that are connected to the WWTP.
Hypothesis:
Advanced oxidation process (AOP) have the potential to degrade the selected compounds: Gemcitabine, 5-Fluorouracil, Cyclophosphamide, Dexamethasone, Doxorubicin, Paclitaxel.
Identification of these compounds using a HPLC-QTOF method is possible.
Objectives:
Development of an analytical method to identify, concentrate and quantitate the selected compounds, focusing on effluent matrix.
Examination of the AOP pilots’ removal efficiency of the selected compounds via the in ‘Tel Ha’Shomer’ hospital.